Sustainable web design is an approach that focuses on creating websites with a minimal Carbon footprint. It considers the entire lifecycle of a website, from its design and development to hosting and maintenance.
Why is Sustainable Web Design Important?
The environmental impact of the internet is significant. Studies show that data centers alone consume a vast amount of energy, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change. By adopting sustainable web design practices, we can collectively reduce our digital footprint and create a greener web.
How to Make Your Website More Sustainable?
There are several steps you can take to make a website more sustainable:
1. Choose Green Hosting
Green website hosting is a more environmental friendly way to host a website. Most green web hosting companies aim to limit their carbon emissions without sacrificing the quality of the services provided.
Green hosting providers power their data centers using renewable energy sources like solar, wind, or geothermal power. This significantly reduces the environmental impact of your website’s operation.
There are certification bodies that certify hosting companies for their greener practices. Knowing what certificates are valid is important when choosing a hosting partner. The two main types of certifications related to green web hosting are Renewable Energy Certificates (REC) and Carbon Offset Certificates (VER).
You can find the Green Web Foundation’s directory for hosting companies committed to using green energies in their data centers.
2. Adhering to Core Web Vital Guidelines
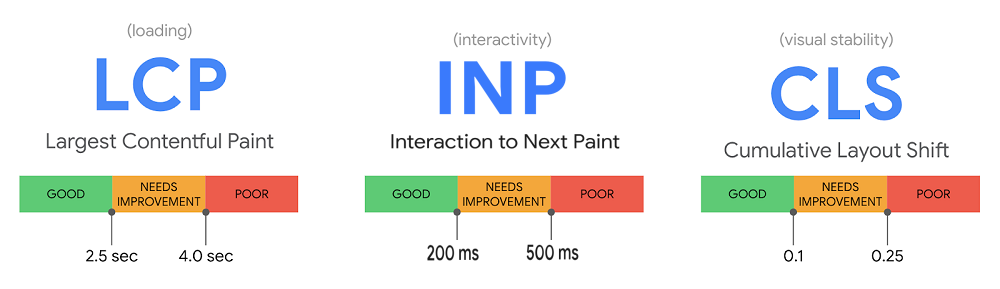
Adhering to Google’s Core Web Vital Guidelines is one way to achieve a greener website. Core Web Vitals aims to reduce the page load time of websites. It considered metrics like LCP, INP, FCP, etc to measure load time.
Consider reducing the time taken to load pages. An efficient page is a greener page!
Use Google’s Page Speed insights to run page load tests for mobile and desktop sites. The tool will list down resources that impact page loading time.
3. Code Optimization
Inefficiently written code can lead to heavier processing demands and higher energy consumption. Review and optimize your website’s code to ensure it runs efficiently.
Minify Code: Minification refers to the process of removing unnecessary or redundant data without affecting how the resource is processed by the browser – e.g. code comments and formatting, removing unused code, using shorter variable and function names, and so on.
Minification reduces the size of CSS or JavaScript code. Even removing white spaces and shortening comments also helps.
- To minify HTML, try HTMLMinifier
- To minify CSS, try CSSNano and csso
- To minify JavaScript, try UglifyJS and Closure Compiler
Obfuscate Code: Obfuscation can lead to smaller file sizes by removing unnecessary whitespace and comments. Obfuscation makes it harder for someone to analyze the code and understand how the program works. This can be useful for protecting proprietary algorithms or intellectual property.
- JavaScript Obfuscator
- UglifyJS
- Obfuscator.io
- Terser
Caching: Implement caching mechanisms to store frequently accessed resources, reducing the server load for repeat visitors.
4. Image & Video Optimization
Large, unoptimized images can significantly increase the file size of your website. This leads to higher energy consumption for storage and transmission, slowing down page load times and frustrating users.
Optimized images not only reduce environmental impact but also improve website performance and user experience.
Compression: There are tools that can compress image files significantly without sacrificing quality. Ensure images are compressed so that the file size is also reduced.
Resizing: Ensure images are sized appropriately for your website layout. There’s no point in storing a high-resolution image if it’s displayed as a thumbnail.
Image Formats: Choose the most suitable format for your images. JPEG is good for photos with a lot of colors, while PNG is better for graphics with sharp lines and text.
Lazy Loading: Load non-critical elements like images or videos only when a user scrolls down to them. This reduces the initial page load weight.
No Autoplays: Ensure videos on the page don’t play automatically. Disabling video autoplay will reduce the bandwidth used.
5. Using Content Delivery Network (CDN)
When a user visits your website, data needs to travel from the server where it’s stored to the user’s device. The greater the distance, the more energy is consumed.
A CDN is a network of geographically distributed servers that store copies of your website’s static content like images, videos, and JavaScript files. When a user requests your website, content is delivered from the nearest CDN server, reducing the distance data needs to travel and saving energy.
CDNs not only improve website sustainability but also enhance loading times for users worldwide by delivering content from the closest server location.
6. Greener Design
Clean, minimalist designs with less clutter typically require less code and data to render, leading to lower energy consumption.
Minimalism and simplicity: A minimalistic approach to design is the road to a sustainable web design. The UI/UX optimized for a better user journey & user experience while using a minimal design philosophy is the key.
Better Site Architecture: Are pages on the sites easily accessible to users? Are thee any orphan pages that are difficult to access by users or search engines? The answer is a lean site architecture. Ensure pages are accessible within 2 to 4 click depth. This ensures users find information they are seeking in less time. Remember, less time = more sustainability.
Usability: Is the website responsive to all sorts of screens and devices? Ensure responsiveness of the website across devices. This will reduce load time, save energy.
7. Sustainable Content
The saying “Content is king/Queen!” doesn’t mean that content should be inflated with a lot of fluff. Addressing the topic to the point is the sustainable way forward.
Clear & Concise writing: Focus on creating content that is clear and concise while keeping file sizes (text, images, videos) optimized. This reduces storage requirements and energy consumption.
Focus on Problem-Solving: Create content that addresses your audience’s needs and solves their problems. This ensures its value endures and reduces the need for repetitive content on similar topics.
Modular Content: Structure your content in a way that allows for easy updates or additions of new information. This promotes long-term usability and avoids the need for complete overhauls.
Evergreen Content: Strive to create content that remains relevant and valuable over time. This reduces the need for frequent updates and content creation, saving resources.
Well-Researched and Accurate: Invest time in thorough research to ensure your content is accurate and reliable. This builds trust with your audience and reduces the need for revisions or corrections later.
Benefits of Sustainable Web Design
There are many benefits to adopting sustainable web design practices:
- Reduced Environmental Impact: By minimizing your website’s energy consumption, you contribute to a greener planet.
- Improved Website Performance: Sustainable design practices often lead to faster loading times and a better user experience.
- Cost Savings: Reduced energy consumption can translate to lower hosting costs.
Sustainable web design is not just a trend; it’s a necessity. By taking these steps, we can all work towards a greener online environment. A sustainable web benefits everyone, reducing our environmental impact and creating a cleaner future for all.
Subscribe to Our Newsletter!


Great article on sustainable web design practices.